
Laser VS Water Jet VS Plasma
How does waterjet cutting work?
Put simply a pump creates high pressure water (50,000-90,000 PSI) that is fed to the cutting head where garnet which is used as an abrasive gets sucked into the water stream which the width of the stream is determined but the cutting head.
Basically this high pressure erodes at the material in a focused area.
How does Laser cutting work?
Fibre lasers are the newest and best option for lasers. These lasers use a diode to create the light which then gets magnified along the fibre until it gets to the cutting head. Once at the cutting head the light is focused into a tiny area where it creates enough heat to melt the material to be cut, Then gas is used to push the melted material away.
How does Plasma cutting work?
Plasma cutting is similar but different to laser cutting. Plasma uses pressurised gas ( Nitrogen, air, oxygen) through a nozzle that is then supplied enough energy from electricity to turn it into a plasma arc. This then melts the material away at around 20,000 degrees c.
What are the ideal jobs for laser?
Laser cutting is generally suited to thinner metal cutting jobs, things like high volume 1-8mm aluminium, mild steel and stainless steel. Most fibre lasers can cut thicker than this but most stick to these sizes.
What are the ideal jobs for waterjet?
Waterjet is the most versatile of the three. Not relying on an arc or heat to cut means it can cut nearly every material. This comes with a down side though as its not as quick at cutting as plasma or fibre laser.
What are the ideal jobs for plasma?
Plasma is most suited to thicker plate processing. plasma is the roughest cut of all three options but it can cut thick mild steel fast! Recently small plasma tables have drastically dropped in price.
What is the best cutting method for small details on thin material?
Laser cutting is the best for really small metal cutting but requires a fairly large piece of metal for it to be cut out of as lasers generally aren’t able to clamp their material and rely on the weight of the sheet to keep it in place.
With waterjet cutting we can work with small material we have ever cut a 25mm2 piece of gold!
How these 3 options compare with different materials
We conducted a test comparing water jet, laser cutting and plasma cutting and have the below data to showcase cutting speeds for the following common types of material.
Mild steel
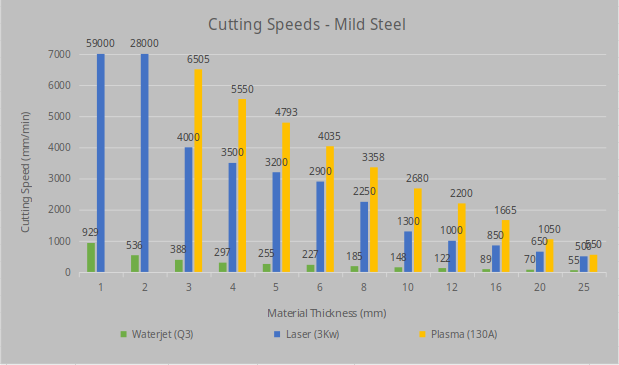
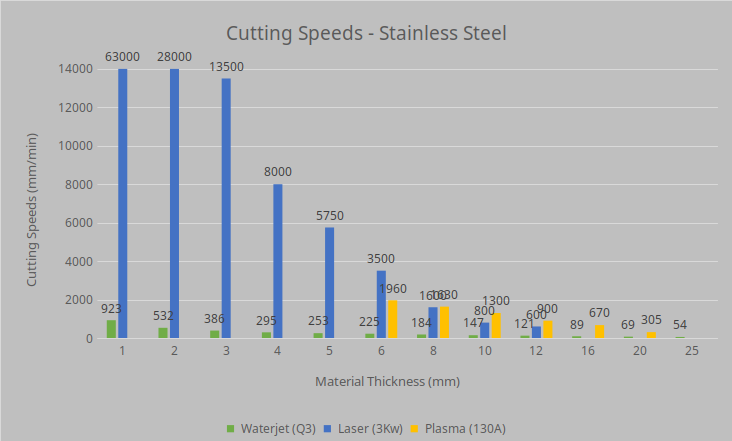
Stainless steel
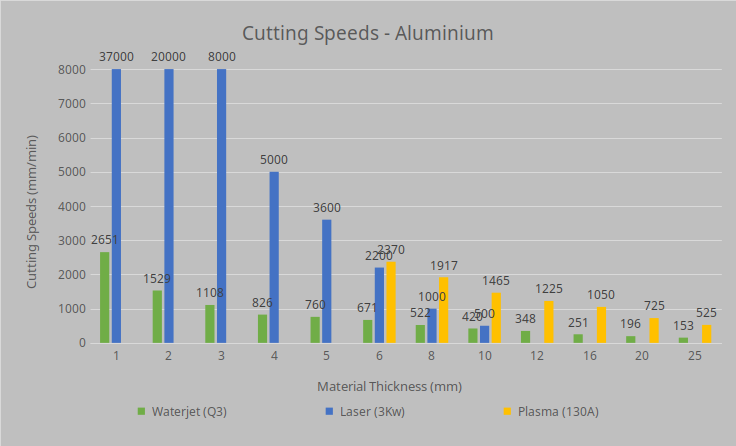
Aluminium
Conclusion
All up in our opinion we would use laser cutting for high volume orders on thin material (under 10mm). Plasma we would use for 10-25mm MS for structural jobs like base plates where the heat and the tolerance isn’t that important ( you can bolt a plate down flat or fit a 10mm bolt in a 12mm hole).
Just about anything else we would recommend waterjet cutting for lower volumes, jobs needing high accuracy or things that cant be cut with a laser or plasma cutter.
If you need help with your next cutting project be sure to get in touch with the MRC team and we will be happy to help!
Also follow us on our social profiles for more updates: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and our YouTube channel




